R&D Products
New Functional Materials
Successfully integrating our fundamental technologies developed over the years, we create new functions, products and businesses, meeting the ever-changing needs of the market. New functional materials are at the core of all research and development, and we continue to explore uncharted territories and discover new possibilities.
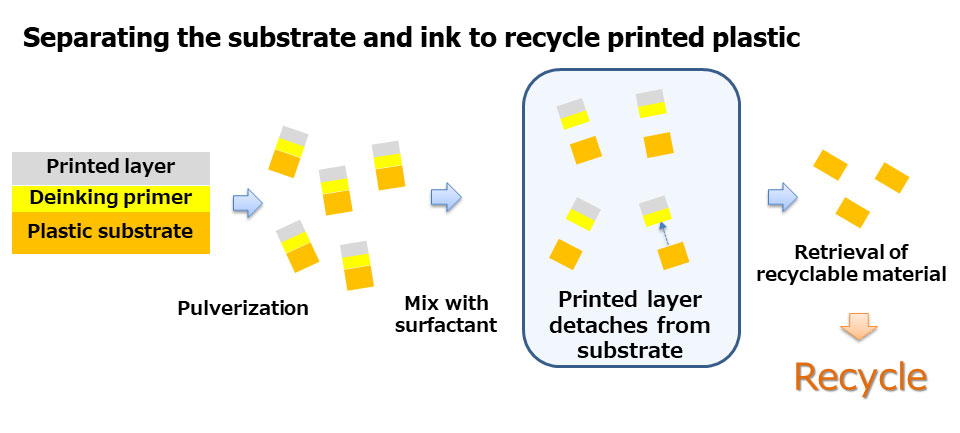
Deinking Primer
Given its high versatility, plastic is used in a large number of fields and industries, however increased environmental awareness has made it necessary to come up with solutions for more sustainable recycling methods. Harima is addressing this need with the development of advanced agents that makes it easy to remove the printed ink on plastics, allowing the plastic to be recycled and reused for a variety of applications. Applying the primer between plastic materials and printed layers at the time of manufacturing makes it easier to detach the latter during recycling processes.
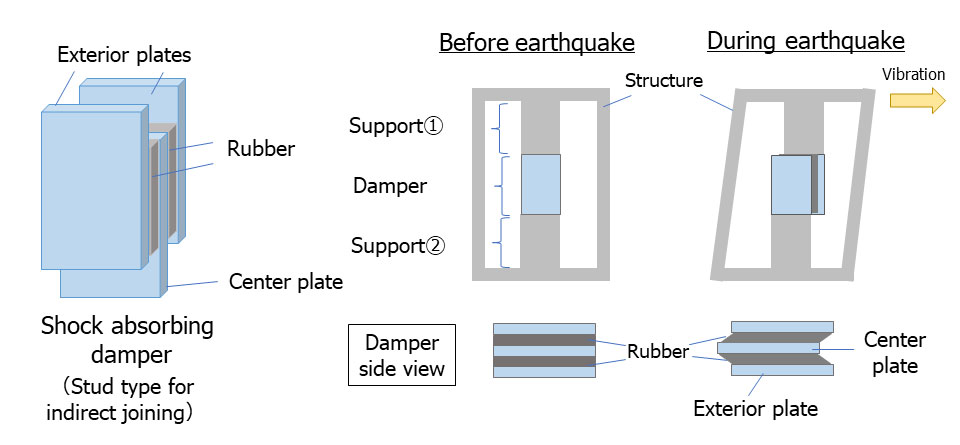
Additives for Rubber Used in Shock Absorbing Dampers
Harima’s rubber additives are employed in shock absorbing dampers used to reduce earthquake damage, where the vibrations are converted into thermal energy. The modified rosin components in the additive initiates a chemical reaction with the rubber and filler materials added to rubber, assisting the shock absorbers in slowing down and reducing the magnitude of vibratory motions.
Materials for Secondary Batteries
Secondary batteries are used in small consumer appliances, compact power supplies, power tools, electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, fuel cell vehicles, energy storage systems (ESS), etc. They are widely employed as a rechargeable power source, of which lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are gaining popularity for their higher energy density output compared to conventional batteries. Harima is developing binder resins used in the production of LIBs, as an adhesive for battery components such as active materials and conductive assistants. These water-based resins are compatible with active materials and adhere well to current collectors, achieving both better functionality and eco-friendliness.
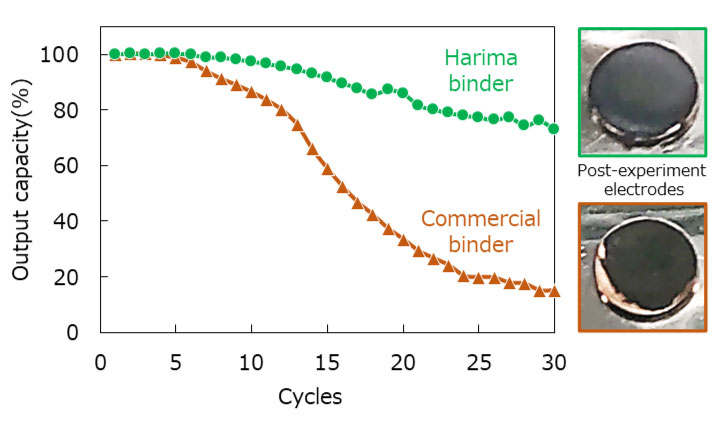
(Evaluation of adhesiveness to negative electrodes)
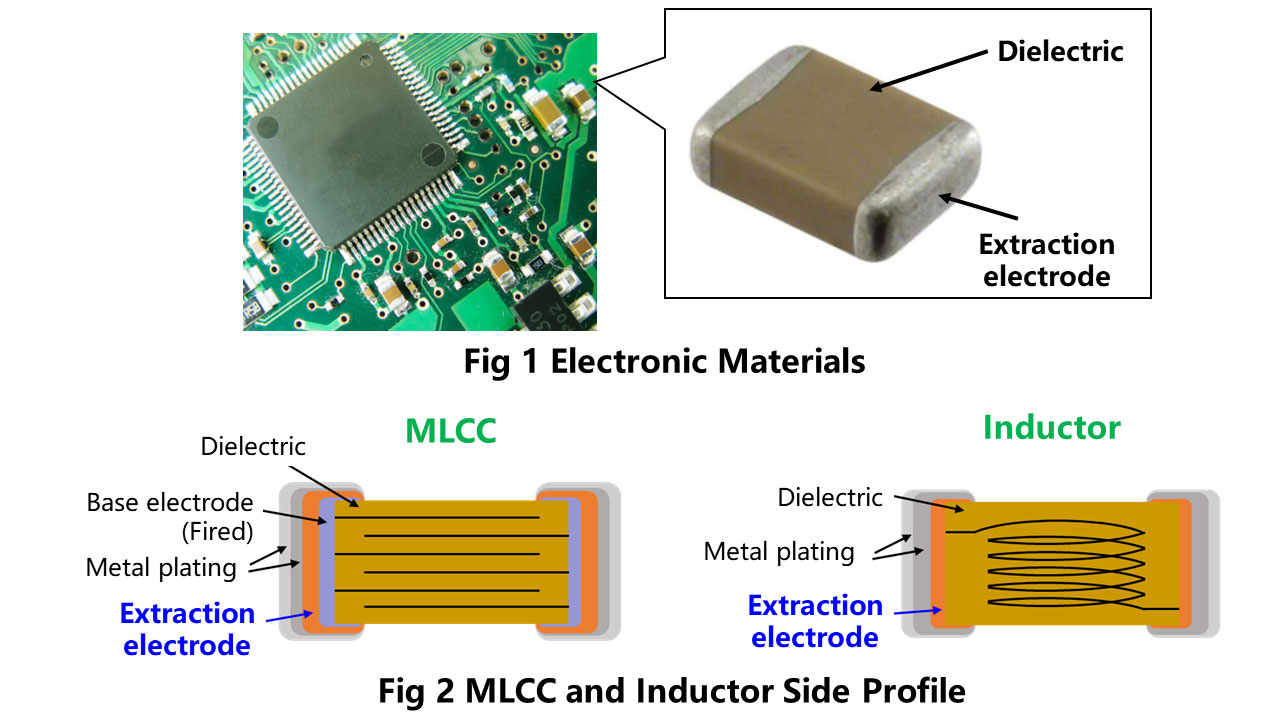
Copper Pastes for Extraction Electrodes
Harima is developing copper pastes for multilayer ceramic chip capacitors(MLCCs)and inductors, which are electronic components used in such products as smartphones and electric vehicles, with growing demand triggered by trends for more compact and sophisticated appliances. Developed using our resin engineering and particle dispersion technologies, these pastes can be used to manufacture extraction electrodes as shown in Fig 2. In addition to outstanding migration properties, the materials adjust to atmospheric conditions and has electrical properties, as well as plating formability and reliability, equivalent or superior to those of conventional silver pastes. Replacing these silver pastes contributes to reducing manufacturing costs of electronic components.